Description
GHK-Cu
GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring tripeptide initially isolated from human blood plasma and later detected in urine and saliva. Studies suggest that GHK-Cu plays a role in supporting tissue repair and immune system function. The peptide has been shown to modulate protein synthesis, enhance the activity of skin fibroblasts, and contribute to skin health. It also exhibits antioxidant activity by reducing free-radical damage and demonstrates antimicrobial potential. Research indicates that GHK-Cu may have additional anti-aging and regenerative effects at the cellular level.
Structures
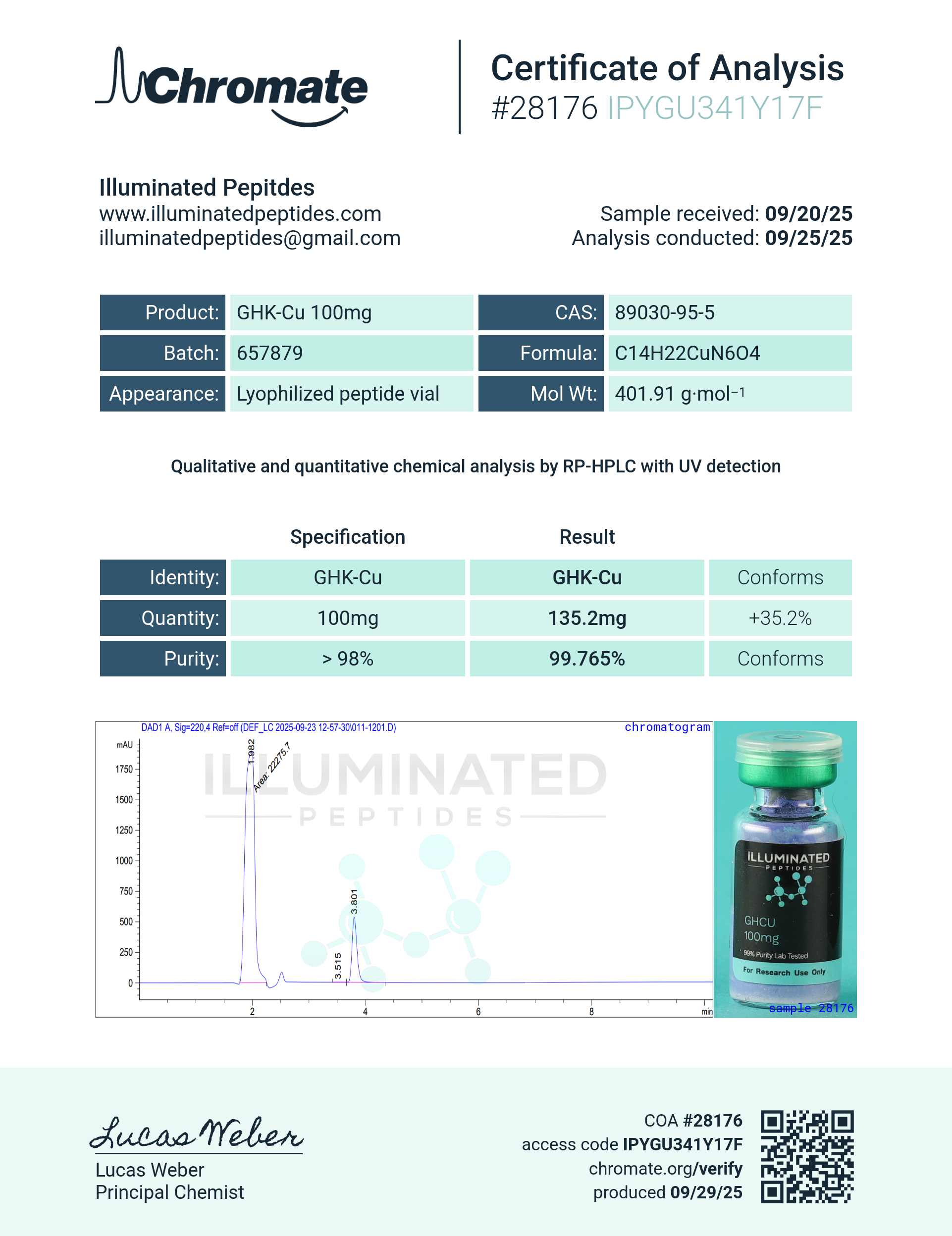
Sequence: Gly-His-Lys. Cu.XHAc
Molecular Formula: C14H23CuN604
Molecular Weight: 401.91 g/mol
PubChem CID:73587
CAS Number: 89030-95-5
GHK-Cu Research
GHK-Cu and Skin Healing
GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring component of human plasma that plays an important role in tissue repair and regeneration. Studies show that GHK-Cu can help regulate the synthesis and breakdown of collagen, glycosaminoglycans, and other extracellular matrix components. These actions are linked to improved skin elasticity, firmness, and resilience.
As a common ingredient in skin-care formulations, GHK-Cu has been associated with visible improvements in skin appearance. It has been shown to help reduce damage caused by sunlight, minimize hyperpigmentation, and soften the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Topical application of GHK-Cu has demonstrated benefits such as enhancing skin density, improving texture, and reducing roughness.
Animal studies suggest that GHK-Cu can accelerate wound closure and improve tissue remodeling after injury. The peptide also appears to support angiogenesis, fibroblast activity, and keratinocyte migration, all of which contribute to faster healing and better quality of repaired tissue.
GHK-Cu and Bacteria
The presence of pathogens in wounds is a major factor that prevents proper healing. GHK-Cu has shown antimicrobial activity, which may reduce the risk of infection by limiting bacterial and fungal growth. This effect is of particular interest in individuals with compromised immune systems or in conditions such as diabetes.
In clinical research, GHK-Cu has been evaluated for its effects on chronic wounds. Results indicate that it can improve wound closure and reduce infection rates compared to standard treatments. This suggests potential for use in cases such as diabetic ulcers and ischemic wounds.
GHK-Cu, Cognition, and Nervous System Function
The loss of neurons due to degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s remains a significant medical challenge. Research indicates that GHK-Cu may help support brain health by influencing pathways linked to neuronal survival and synaptic repair. It has been found in high concentrations within the brain, particularly in regions associated with memory and learning.
Studies suggest that GHK-Cu can reduce inflammation within the nervous system, promote outgrowth of neurons, and regulate stress responses in brain tissue. These effects may contribute to slowing the decline associated with neurodegeneration.
One proposed mechanism is that GHK-Cu supports neuroprotection by modulating gene expression linked to cell survival pathways. It also promotes the clearance of damaged cells and the regeneration of healthy neuronal connections.
GHK-Cu and Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy often causes damage to healthy tissues, leading to side effects such as inflammation and fibrosis. Experimental models suggest that GHK-Cu can reduce tissue damage by protecting cells from oxidative stress and by moderating inflammatory responses.
In the lungs, GHK-Cu has been shown to reduce fibrosis and improve tissue recovery following injury. These protective effects may help limit long-term damage and improve respiratory function after exposure to harmful agents.
GHK-Cu appears to act by regulating pathways that influence cytokine activity and tissue remodeling. By supporting balanced immune responses, it may help protect normal tissues during chemotherapy and other treatments that generate oxidative damage.
GHK-Cu and Pain Reduction
The use of GHK-Cu has also been explored in the context of pain relief. Experimental studies suggest that administration of GHK-Cu can produce analgesic effects, particularly in cases of chronic or neuropathic pain. This may occur through modulation of inflammatory mediators and interaction with opioid receptors.
Research indicates that GHK-Cu may lower the perception of pain while also reducing swelling and tissue sensitivity. These findings point to potential applications in the management of inflammatory pain as well as discomfort linked to tissue injury.
GHK-Cu has demonstrated good tolerability with minimal adverse effects in laboratory settings. Due to its stability and bioavailability, it is considered a promising candidate for future therapeutic applications.
Note: GHK-Cu is studied for research purposes only. It is not approved for human consumption