Description
What Is Ipamorelin?
Ipamorelin is a synthetic pentapeptide belonging to the class of growth hormone (GH) secretagogues. It functions as a selective agonist of the ghrelin receptor, enabling it to stimulate the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. Unlike earlier compounds in the same category, Ipamorelin is noted for its precision in targeting GH release while minimizing effects on other hormones such as cortisol and prolactin.
Ipamorelin Structure
sequence: Aib-His-(D-2-Nal)-(D-Phe)-Lys-NH₂.
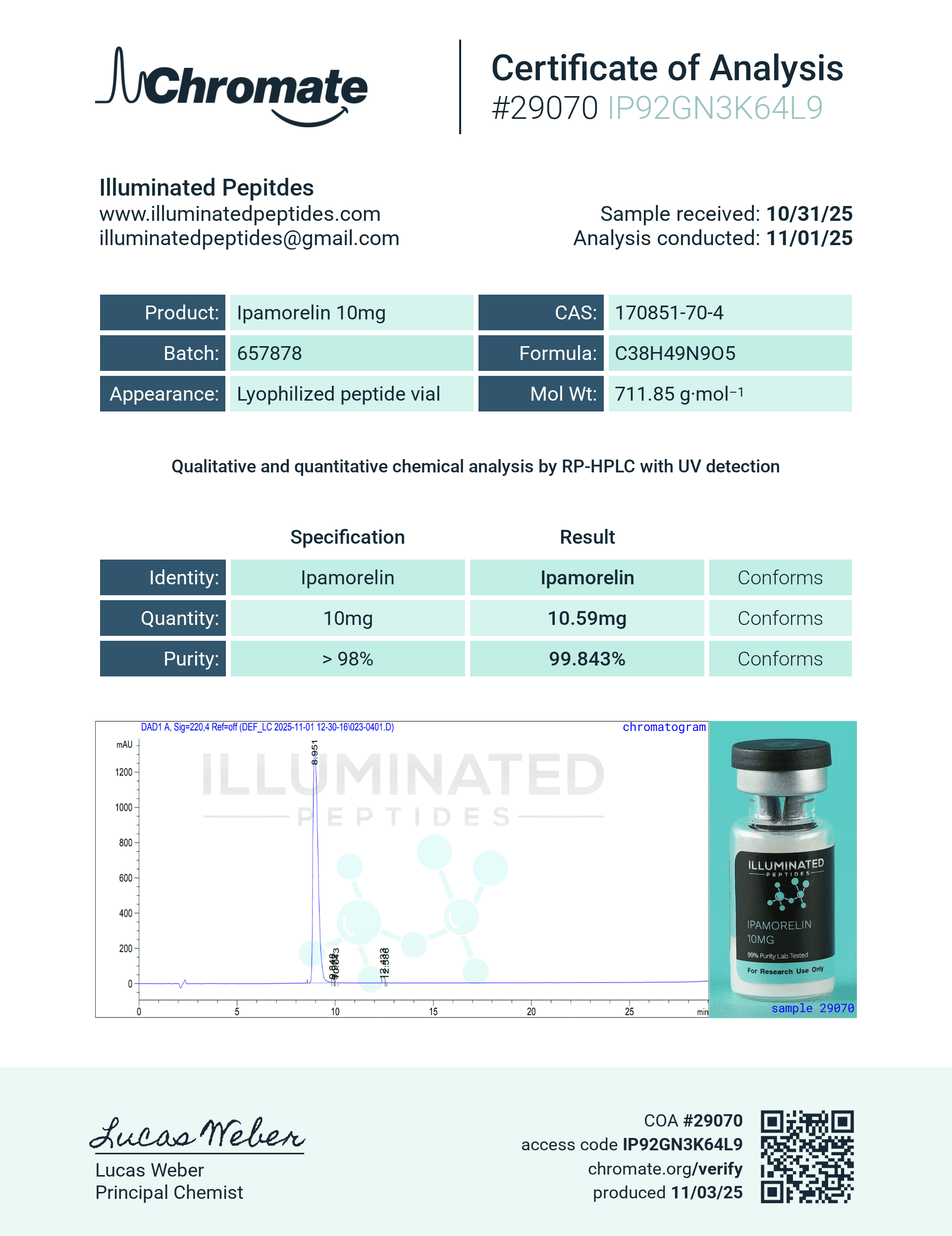
Molecular formula: C₃₈H₄₉N₉O₅.
Molecular weight: ≈ 711.9 g·mol⁻¹.
PubChem CID: 9831659.
CAS number: 170851-70-4.
Ipamorelin Research
Ipamorelin and Negative Corticosteroid Effects
One of the distinctive findings in Ipamorelin studies is its ability to promote growth hormone release without causing a corresponding rise in cortisol levels. This selectivity is significant because excessive corticosteroid activity is often linked to negative outcomes such as immune suppression, weight gain, and metabolic disturbances. Ipamorelin’s reduced interaction with adrenal function allows researchers to study GH-related processes without the confounding influence of corticosteroid spikes.
Ipamorelin and Bone Health
Preclinical investigations have shown that Ipamorelin may encourage bone formation and density improvements through growth hormone-mediated pathways. Enhanced GH secretion is associated with elevated levels of IGF-1, which plays a direct role in bone mineralization and skeletal strength. Researchers are particularly interested in whether such effects could provide insights into treating conditions related to bone fragility.
Ipamorelin and Muscle Growth
Ipamorelin is frequently studied in connection with skeletal muscle development. By stimulating GH release, it indirectly promotes protein synthesis and lean tissue growth in experimental models. These properties make it an important compound for investigating muscle recovery, sarcopenia, and other research areas involving tissue regeneration.
Ipamorelin and Diabetes
Research has explored the role of Ipamorelin in metabolic health, particularly glucose regulation. Since GH can influence insulin sensitivity and carbohydrate metabolism, studies are examining whether Ipamorelin’s effects on GH release have implications for understanding diabetes. Findings suggest that while GH has complex interactions with blood sugar levels, selective secretagogues like Ipamorelin may help clarify the relationship between growth hormone and insulin activity.
Studied for Treatment of Post-Operative Ileus
Post-operative ileus (POI) is a temporary impairment of bowel function that often occurs after abdominal surgery, leading to discomfort and delayed recovery. Research indicates that Ipamorelin, due to its ghrelin receptor activity, may enhance gastrointestinal motility. By stimulating receptors in the gut, the peptide shows potential to shorten the duration of POI in clinical settings.
In addition, studies have highlighted that Ipamorelin achieves this effect without triggering excessive side effects commonly observed in other GH secretagogues. Its targeted mechanism makes it an intriguing candidate for further research into post-surgical recovery and gastrointestinal disorders, although more controlled trials are necessary to fully evaluate its safety and efficacy.
Ipamorelin as Ghrelin Receptor Probe
Beyond therapeutic studies, Ipamorelin is widely utilized as a research probe for ghrelin receptor function. Its selective agonism provides scientists with a precise tool to investigate how ghrelin pathways regulate appetite, hormone release, and gastrointestinal motility. This makes it a valuable compound for advancing basic science as well as applied medical research.