Description
What is Retatrutide?
Retatrutide is an investigational peptide drug designed as a triple agonist, targeting the GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors. Unlike single-pathway agents, Retatrutide engages multiple metabolic signaling routes simultaneously, giving it a unique role in research exploring glucose regulation, appetite control, and energy balance.
Early studies suggest Retatrutide may significantly influence body weight regulation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid metabolism, making it a compound of strong interest in metabolic and obesity-related research. Beyond weight management, ongoing investigations are examining its potential relevance in diabetes and other metabolic disorders, highlighting its promise as a broad-spectrum metabolic modulator.
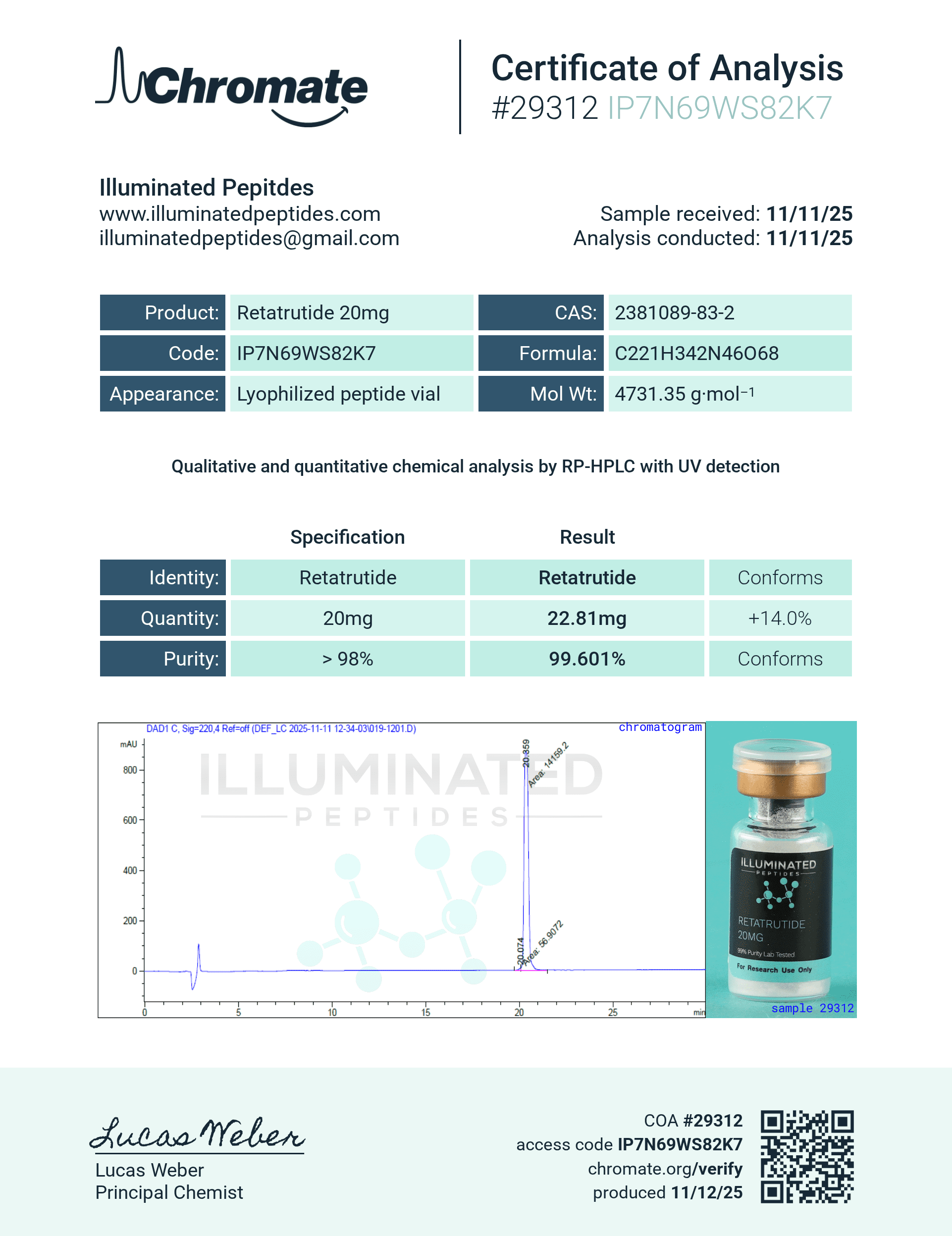
Retatrutide Structure
Sequence: Peptide-based GLP-1/GIP/Glucagon receptor agonist
Molecular Formula: C267H401N65O81
Molecular Weight: 5927.9 g/mol
PubChem CID: 162949366
CAS Number: 2381089-83-2
Retatrutide Research
Retatrutide and Weight Management
Retatrutide has gained significant attention for its strong impact on body weight regulation. As a triple agonist of GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors, it stimulates multiple hormonal pathways that reduce appetite, increase satiety, and enhance energy expenditure. Early clinical studies show substantial weight loss outcomes, often exceeding results seen with single-receptor agonists. This positions Retatrutide as a promising compound in obesity and metabolic research.
Retatrutide and Diabetes
Beyond weight reduction, Retatrutide is being studied for its potential role in type 2 diabetes management. By improving insulin sensitivity, reducing blood glucose levels, and modulating pancreatic hormone activity, the compound offers insights into more effective glycemic control. Its unique receptor profile allows it to impact both insulin secretion and glucagon balance, critical factors in diabetes research.
Retatrutide and Metabolic Regulation
One of Retatrutide’s defining characteristics is its ability to modulate overall metabolism. Preclinical findings suggest it enhances lipid utilization, reduces fat storage, and shifts energy balance toward improved metabolic efficiency. These effects make it a valuable candidate for exploring broader metabolic disorders, including dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome.
Retatrutide and Cardiovascular Health
Research has also begun to investigate Retatrutide’s influence on cardiovascular parameters. By lowering body weight, improving glucose control, and reducing risk factors like cholesterol and triglycerides, Retatrutide may contribute to better heart health outcomes. While this field of study is still in early stages, the compound’s triple agonist mechanism could play a protective role in cardiometabolic disease models.
Retatrutide and Future Applications
The versatility of Retatrutide lies in its multi-pathway activity, which opens the door to applications beyond obesity and diabetes. Researchers are examining whether its receptor profile can impact conditions such as fatty liver disease (NAFLD/NASH), endocrine regulation, and long-term metabolic resilience. Continued studies will help clarify its potential across these diverse areas.