Description
What is TB-500?
TB-500, also known as Thymosin Beta-4, is a synthetic peptide originally derived from the naturally occurring protein thymosin beta found in human tissues. Unlike many compounds that act indirectly, TB-500 works by directly modulating cellular pathways involved in tissue repair, regeneration, and inflammation. Specifically, it influences actin polymerization and cell migration, key processes for wound healing and angiogenesis.
Research shows that TB-500 can promote recovery in injured tissues, accelerate wound closure, and improve flexibility and endurance in preclinical models. Beyond its regenerative focus, it has also been studied for potential roles in reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular and immune function. These findings make TB-500 a peptide of broad scientific interest in regenerative medicine and tissue repair research.
TB-500 Structure
Sequence: Ac-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro-Val-Thr-Lys-Asp-Ala-Ala-Glu-Ile-Glu-Lys-Glu-Lys-Val-Val-Glu-Glu-Asp
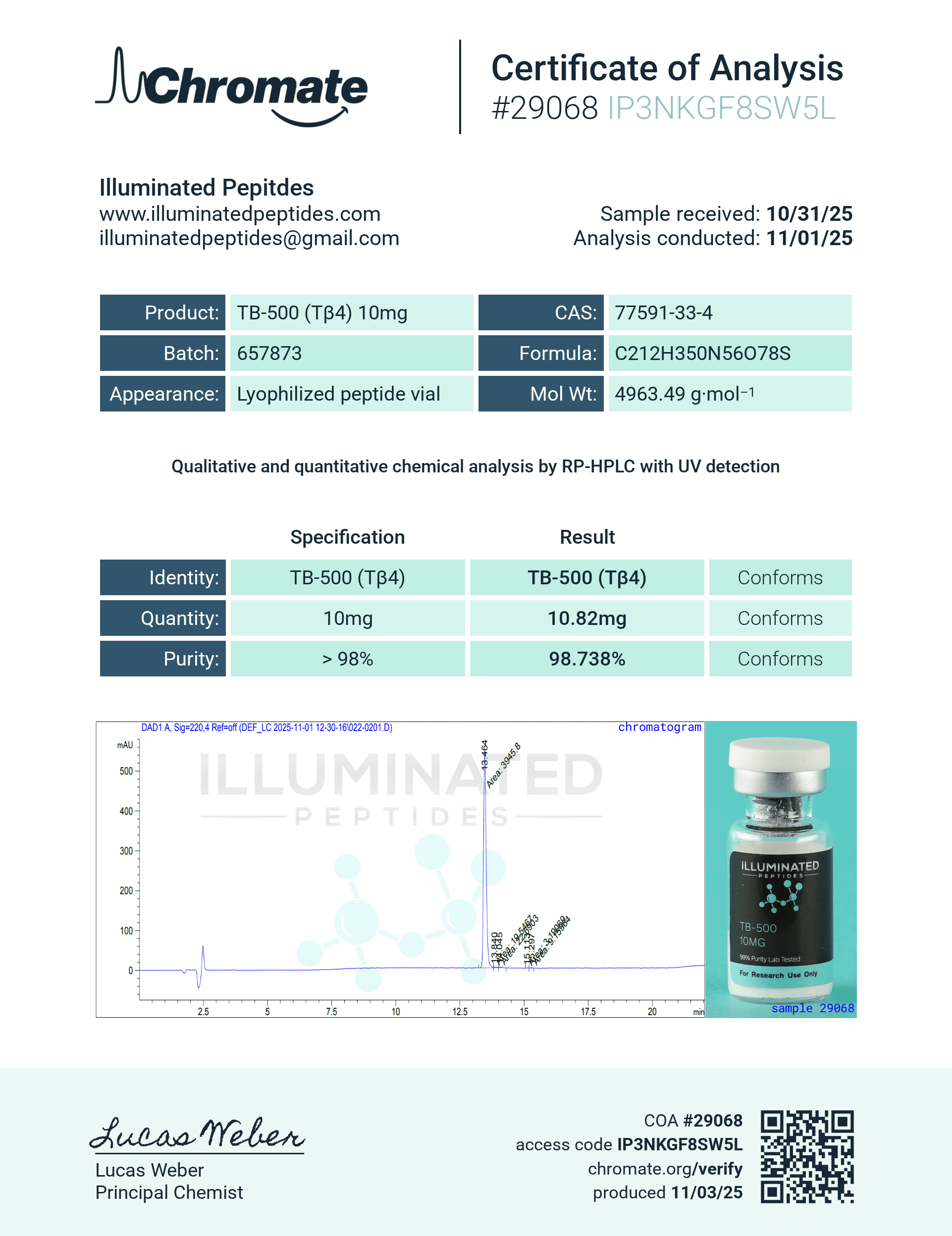
Molecular Formula: C212H350N56O78S
Molecular Weight: 4963.5 g/mol
PubChem CID: 16234388
CAS Number: 77591-33-4
TB-500 Research
TB-500 and Tissue Repair
TB-500 is most widely recognized for its role in promoting tissue repair and wound healing. Unlike agents that act indirectly through systemic pathways, TB-500 directly influences actin polymerization and cell migration, which are crucial for repairing damaged tissues. This mechanism enables cells to move efficiently to sites of injury and facilitates faster tissue regeneration.
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that TB-500 accelerates wound closure, enhances recovery from muscle and tendon injuries, and supports cellular repair in various tissues. By promoting angiogenesis, it improves oxygen and nutrient delivery to healing areas, which is essential for effective regeneration.
These findings underscore TB-500’s potential importance in regenerative medicine research, offering a model for understanding cellular recovery processes and the molecular regulation of tissue repair.
TB-500 and Inflammation Modulation
Research indicates that TB-500 can reduce inflammation in damaged tissues. By modulating inflammatory pathways, it helps create an environment conducive to repair and regeneration. Reduced inflammation can also decrease pain and swelling associated with injuries, which further supports recovery.
Studies in animal models have shown that TB-500 administration lowers markers of inflammatory cytokines in injured muscles and connective tissues. This anti-inflammatory profile makes it a valuable compound for investigating therapies for inflammatory and autoimmune-related tissue damage.
TB-500 and Musculoskeletal Health
TB-500 has been explored for its benefits in musculoskeletal health, particularly in improving flexibility, reducing scarring, and accelerating recovery from strains or tears. It enhances cellular migration and promotes the deposition of structural proteins in connective tissues, contributing to stronger and more resilient muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Experimental studies suggest that repeated administration of TB-500 can significantly improve the healing time of tendon injuries and reduce fibrosis in damaged areas. Additionally, its impact on angiogenesis supports better nutrient flow to musculoskeletal structures, enhancing overall recovery.
TB-500 and Cardiovascular Support
Some studies have investigated TB-500’s influence on cardiovascular tissue repair and angiogenesis. By promoting new blood vessel formation, it may improve circulation to areas affected by ischemia or injury.
Animal research has shown that TB-500 can support endothelial cell function and aid in the repair of cardiac tissue following damage. These findings are preliminary but indicate that TB-500 may have broader applications in tissue regeneration beyond musculoskeletal recovery.
TB-500 and Organ Health
Beyond muscles and tendons, TB-500 may benefit overall organ health by enhancing cellular repair mechanisms and reducing tissue stress. Experimental studies highlight its potential in accelerating recovery in liver, kidney, and other organ tissues following injury or metabolic stress.
Its ability to modulate actin dynamics and reduce inflammation at the cellular level makes TB-500 a compound of interest for researchers studying organ repair, regenerative medicine, and age-related tissue degeneration.